创建一个timerfd,然后由epoll 监听其事件对应做相应的事件处理,下面是一个简单的demo
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h> // close()
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
#define EPOLL_LISTEN_CNT 256
#define EPOLL_LISTEN_TIMEOUT 500
int main()
{
// create epoll fd
int epfd = epoll_create(EPOLL_LISTEN_CNT);
if (epfd < 0)
{
printf("[ERROR]: epoll_create error[%d:%d:%s]", epfd, errno, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
// set itimerspec
struct itimerspec new_value;
new_value.it_value.tv_sec = 2;
new_value.it_value.tv_nsec = 0;
new_value.it_interval.tv_sec = 1;
new_value.it_interval.tv_nsec = 0;
// create timerfd
int tmfd = timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, TFD_NONBLOCK | TFD_CLOEXEC);
if (tmfd < 0)
{
printf("[ERROR]: epoll_create error[%d:%d:%s]", tmfd, errno, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
// set timer
int ret = timerfd_settime(tmfd, 0, &new_value, NULL);
if (ret < 0)
{
printf("[ERROR]: epoll_create error[%d:%d:%s]", ret, errno, strerror(errno));
close(tmfd);
return -1;
}
// add timerfd to epollfd
struct epoll_event event;
memset(&event, 0, sizeof(event));
event.data.fd = tmfd;
event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
ret = epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, tmfd, &event);
if (ret < 0)
{
printf("[ERROR]: epoll_create error[%d:%d:%s]", ret, errno, strerror(errno));
close(tmfd);
return -1;
}
// handle event
struct epoll_event events[EPOLL_LISTEN_CNT];
memset(events, 0, sizeof(events));
uint64_t total_exp = 0;
while (1)
{
// wait epoll event
int fd_cnt = epoll_wait(epfd, events, EPOLL_LISTEN_CNT, EPOLL_LISTEN_TIMEOUT);
for (int i = 0; i < fd_cnt; i++)
{
int sfd = events[i].data.fd;
if ((events[i].events & EPOLLIN) &&(sfd == tmfd))
{
// handle timerfd
uint64_t exp = 0;
// 可以用read函数读取计时器的超时次数,该值是一个8字节无符号的长整型
read(sfd, &exp, sizeof(uint64_t));
// 打印次数
total_exp += exp;
printf("read: %llu, total: %llu\n", (unsigned long long)exp, (unsigned long long)total_exp);
// 打印当前时间
struct timespec curr;
if (clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &curr) == -1)
{
printf("clock_gettime error\n");
return -1;
}
printf("%ld.%03ld\n", curr.tv_sec, curr.tv_nsec);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
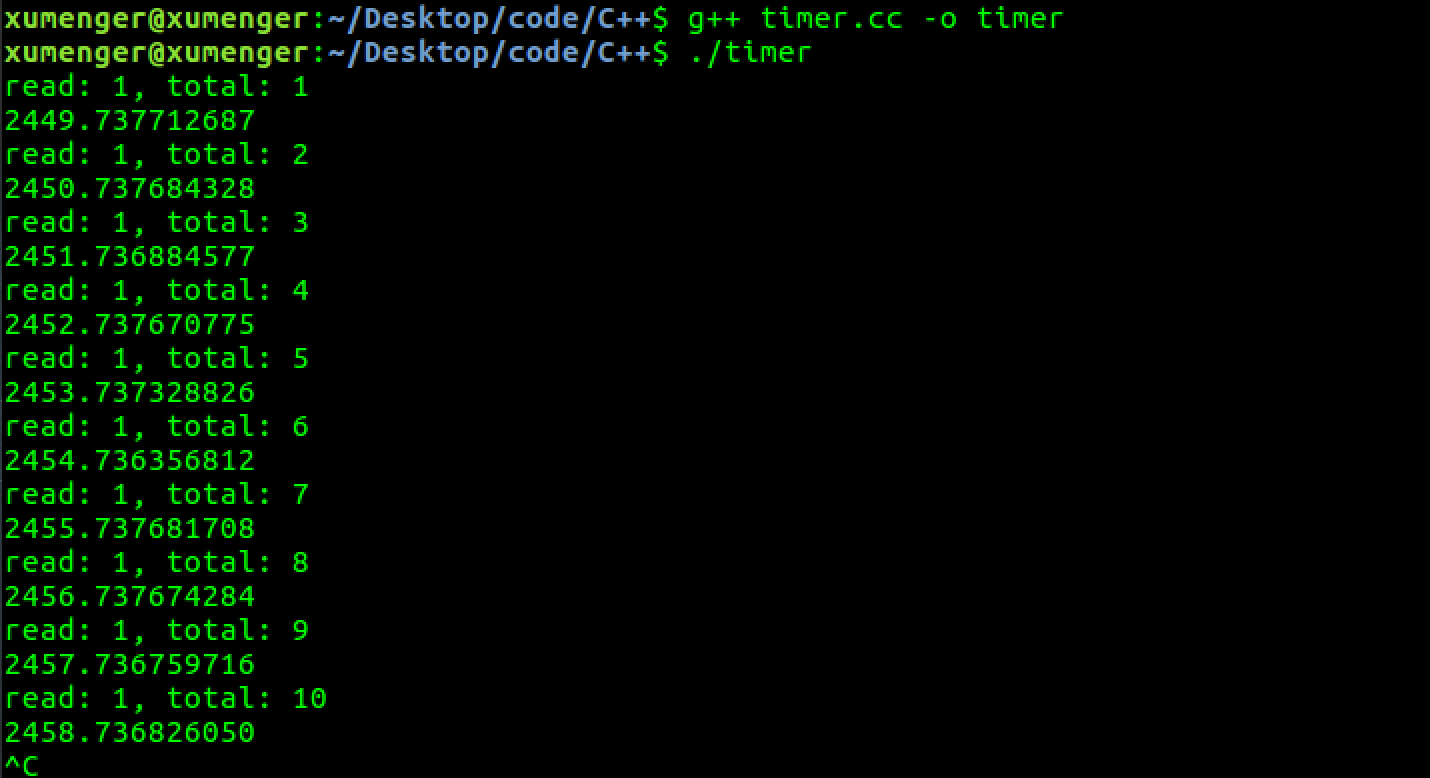
编译运行的效果如下,每隔一秒钟事件触发一次
timespec 与itimerspec
struct timespec {
time_t tv_sec; // Seconds
long tv_nsec; // Nanoseconds
};
struct itimerspec {
struct timespec it_interval; // 定时间隔周期
struct timespec it_value; // 第一次超时时间
}
timerfd_create()
/**
* CLOCK_REALTIME: 系统实时时间,随系统实时时间改变而改变,即从UTC1970-1-1 0:0:0 开始计时,中间时刻如果系统时间被用户改成其他,则对应的时间相应改变
* CLOCK_MONOTONIC: 从系统启动这一刻起开始计时,不受系统时间被用户改变的影响
*
* TFD_NONBLOCK: 非阻塞模式
* TFD_CLOEXEC: 表示当程序执行exec 函数时本fd 将被系统自动关闭,表示不传递
*/
int tmfd = timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, TFD_NONBLOCK | TFD_CLOEXEC);
timerfd_settime()
/**
* fd: 参数fd是timerfd_create 函数返回的文件句柄
* flags:参数flags 为1 代表设置的是绝对时间(TFD_TIMER_ABSTIME 表示绝对定时器);为0 代表相对时间
* new_value: 参数new_value 指定定时器的超时时间以及超时间隔时间
* old_value: 如果old_value 不为NULL,old_vlaue 返回之前定时器设置的超时时间
*
* it_interval 不为0则表示是周期性定时器
* it_value 和it_interval都为0表示停止定时器
*/
int ret = timerfd_settime(tmfd, 0, &new_value, NULL);
