
这种基于观察方向 + 法线方向实现的描边效果,出来的描边效果不“硬”,反而适合水墨渲染的那种随意感!
公式解释
下面的代码中最重要的就是
v2f vert (appdata_base v)
{
v2f o;
// 将模型空间的点转换到裁剪空间
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
// ObjSpaceViewDir() 这个函数输入一个模型空间的顶点位置,返回模型空间中从该点到摄像机的观察方向,即 view方向
float3 ObjViewDir = normalize(ObjSpaceViewDir(v.vertex));
// 标准化法线向量
float3 normal = normalize(v.normal);
// 两个标准向量点乘,计算得到两个向量夹角的cos 值
// 向量垂直,点乘为0;向量同向,点乘为1;夹角为锐角,点乘大于0;夹角为钝角,点乘小于0
float factor = step(_Outline, dot(normal, ObjViewDir));
o.color = float4(1, 1, 1, 1) * factor;
return o;
}
另外step() 函数的逻辑可以用下面的伪代码表示
step (a, x)
{
if (x < a)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return 1;
}
}
另外顺便介绍一下常用的lerp()、smoothstep() 函数
lerp() 函数
lerp() 函数伪代码如下:
lerp(a, b, w)
{
return a + w*(b-a)
}
当w = 0 时,返回a,当w = 1 时返回b,否则返回对a 和b 的差值,w 越接近0,返回结果越接近a,w 越接近1,返回结果🈷越接近1,通常用来计算一些渐变量
smoothstep() 函数
smoothstep() 可以用来生成0 到1 的平滑过渡值,它也叫平滑阶梯函数。smoothstep定义是
float smoothstep(float a, float b, float x)
{
x = clamp((x - a) / (b- a), 0.0, 1.0);
return x * x * (3 - 2 * x);
}
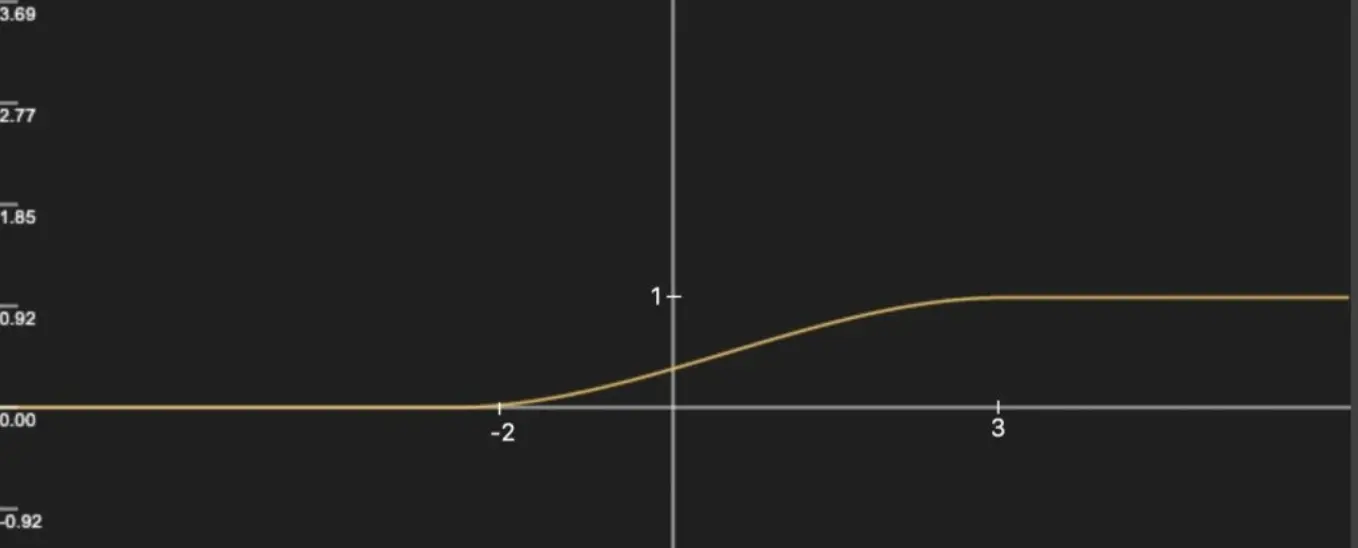
在a < b 的情况下,当x < a 时,返回0,当x > b 时,返回1,否则在0 和1 之间平滑过渡,比如smoothstep(-2, 3, x) 的函数图像:
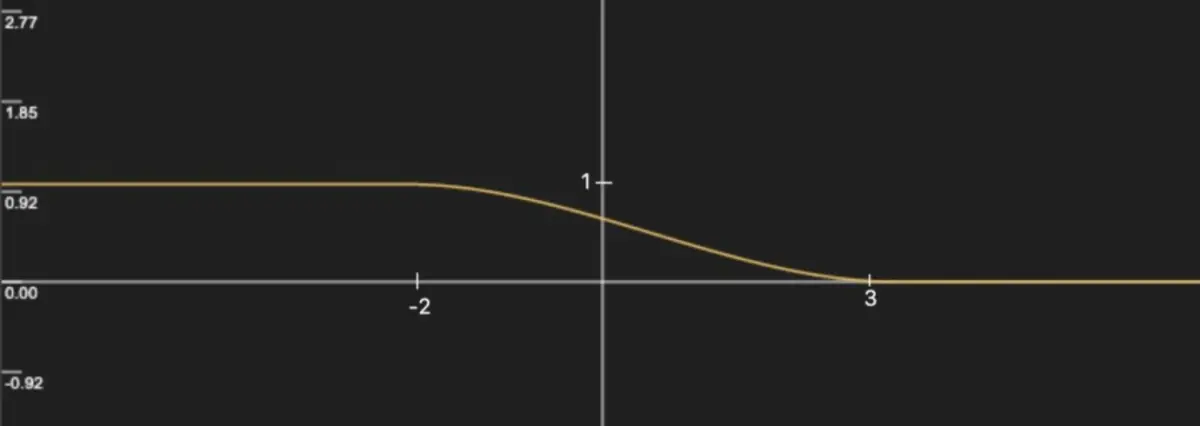
在a > b 的情况下,当x < b 时,返回1,当x > a 时,返回0,否则在1 和0 之间平滑过渡,交换上述a 和b 的位置,可以得到 smoothstep(3, -2, x) 的函数图像 :
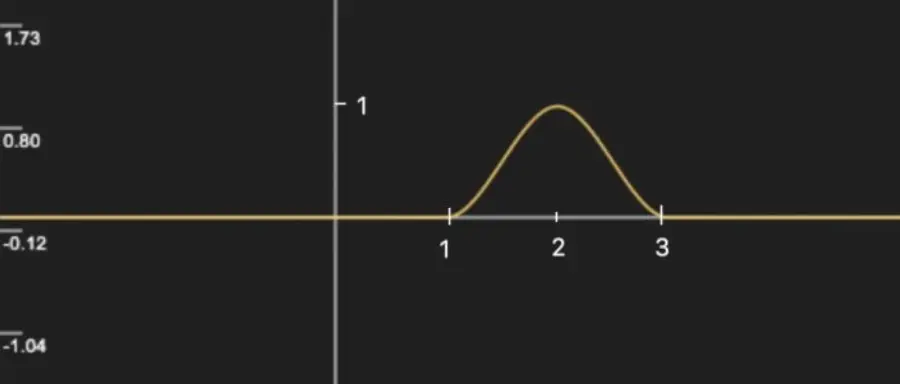
两个smoothstep 进行减法运算可以得到一些波形图,例如smoothstep(1, 2, x) - smoothstep(2, 3, x) 的函数图像
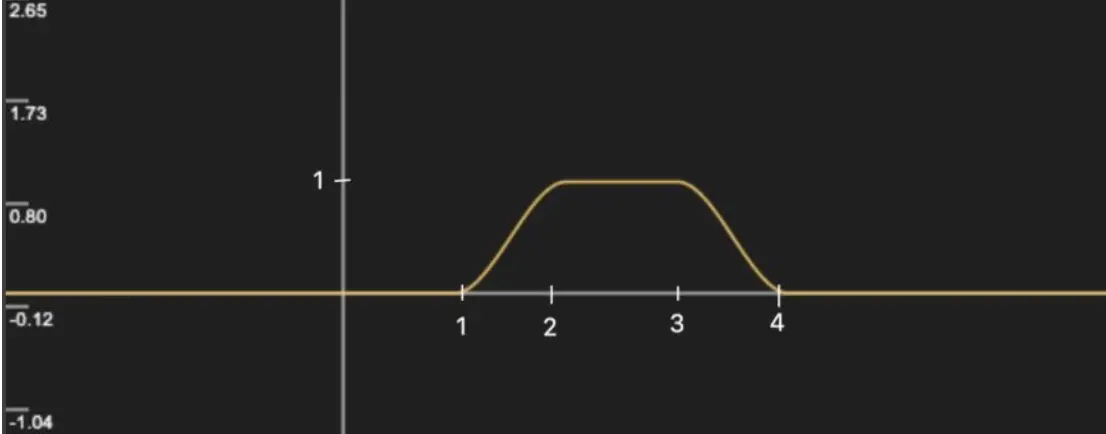
想要增加波峰的持续宽度,可以构造smoothstep(1, 2, x) - smoothstep(3, 4, x),图像如下:
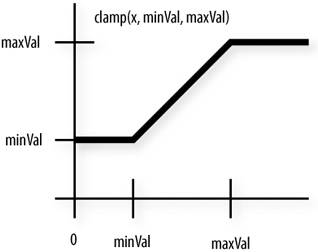
clamp() 函数
用来将某个值“钳”住、限制在某个区间(min~max)
float lamp(float x, float min, float max)
{
if (x > max)
return max;
if (x < min)
return min;
return x;
}
代码演示
// 基于观察角度和表面法线
Shader "Unlit/Outline_Cull_View_Normal"
{
Properties
{
_Outline ("Outline", Range(0, 1)) = 0.1
}
SubShader
{
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" "RenderPipeline" = "UniversalPipeline"}
// 渲染固定颜色(缺少光照模型、贴图处理等)
Pass
{
Cull Back
Tags { "LightMode" = "SRPDefaultUnlit" }
CGPROGRAM
fixed4 _Color;
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
float _Outline;
struct v2f
{
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
fixed4 color : COLOR;
};
v2f vert (appdata_base v)
{
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
float3 ObjViewDir = normalize(ObjSpaceViewDir(v.vertex));
float3 normal = normalize(v.normal);
float factor = step(_Outline, dot(normal, ObjViewDir));
o.color = float4(1, 1, 1, 1) * factor;
return o;
}
float4 frag(v2f i) : SV_Target
{
return i.color;
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack "Diffuse"
}
